Heavy-Hitter Hardware: Bar Equipment
by David Klemt
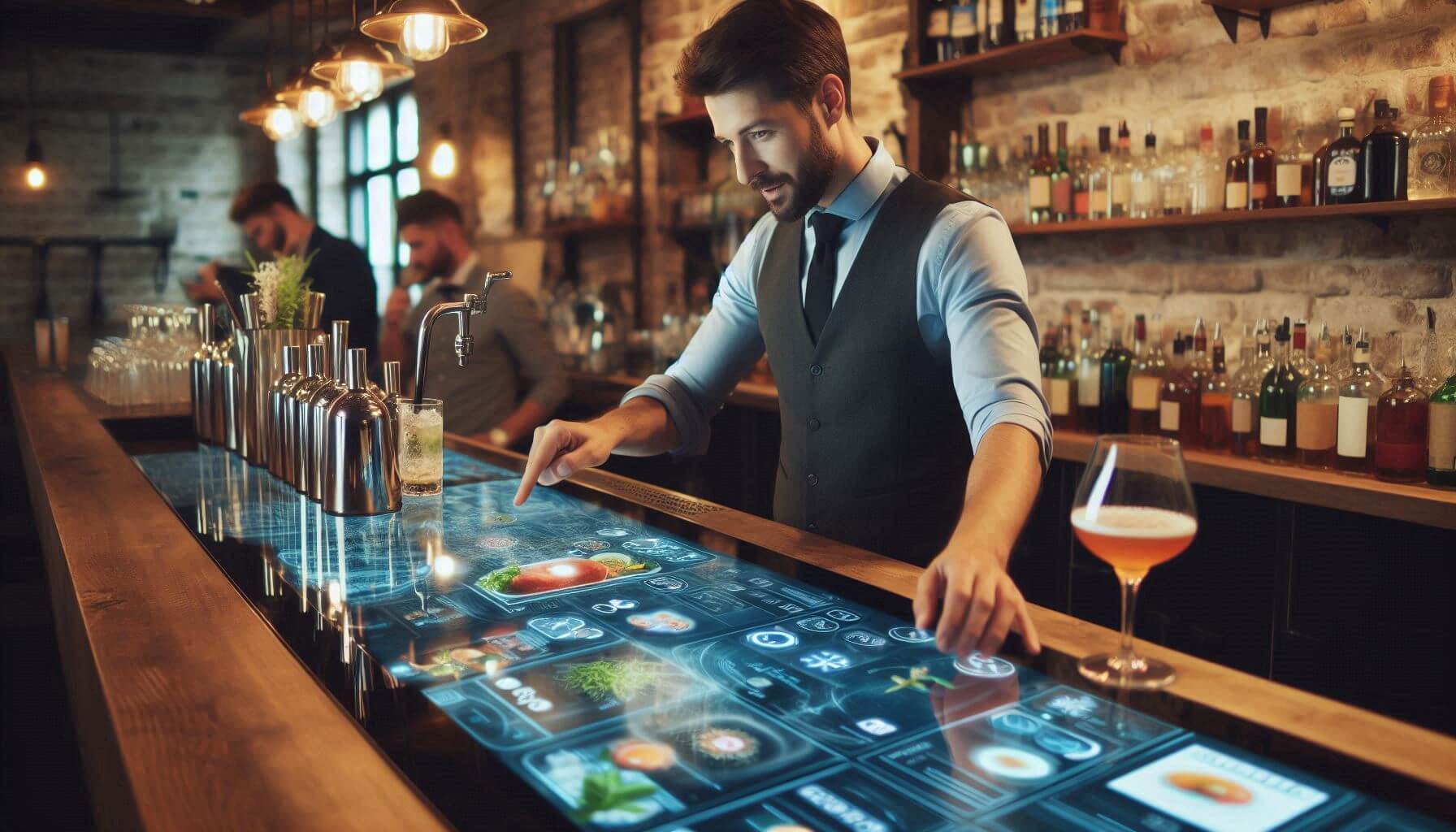

In how many years do we all think this type of bar top will be more mainstream? Note: AI-generated image.
We have clients planning to open their new concepts in 2025, so we’re sharing bar equipment innovations to inspire you and your bar plans.
There’s a lot to consider when transforming the vision for your space into a brick-and-mortar reality. Some of it is fun and exciting—drink menus and recipes, logo and branding, theme—and some is more technical (read: less exciting).
Of course, if you’re into design, precision, and equipment, selecting hardware and planning layout is probably fairly exciting. It is to us at KRG Hospitality!
To be clear, you won’t find bar tools in this article. I think the Flavour Blaster is rad, and I’ve been to my fair share of bars that use rotovaps, centrifuges, immersion circulators, liquid nitrogen, and sous vide machines.
Instead, I’m talking about the hardware that creates each bartender’s workstation; the cocktail cockpits that help ensure consistency, elevate the guest experience, and generate revenue.
Speaking of which…
Ergonomic Bar Stations
Roughly a decade ago, Perlick’s engineers partnered with one of the world’s most famous bartenders.
The company has been designing and manufacturing commercial bar equipment for decades. In 2015, they took their manufacturing to an entirely new level with the Tobin Ellis Signature Cocktail Station.
If you don’t know Tobin Ellis, definitely Google him after you finish this article. What you need to know now is that he has always been a proponent of proper bar design. I’ve attended many of his speaking appearances over the years, and he has driven one key point home during almost every presentation: Bartenders need to be involved in the bar design process.
Simply put, many interior designers have never worked behind a bar. Often times, they design bars that are inefficient; it’s just a reality of this business.
When Perlick and Ellis unveiled their cocktail station, it changed the game. Putting an emphasis on ergonomics and efficiency was—and still is—transformative.
Benefits
Bartenders who aren’t blowing out their backs over the course of every shift are happier and healthier. Ergonomic bar stations are designed to fight strain, pain, hyperextension injuries, and fatigue.
Further, not having to leave their station to find tools, drinkware, bottles, and ingredients makes bartenders more efficient, and faster.
I shouldn’t have to point out that bar owners and operators should want their bartenders to work without risking damage to their bodies. Nor should I have to point out that a happy bartender improves the guest experience.
Of course, this goes for every role in a hospitality business. There are choices and investments owners and operators can (and should) make at the start of their projects to improve the employee experience. There should be no division between the guest and team experience; both are paramount, and both must be valued.
While ergonomic bar stations aren’t cheap, their pricing is fair in contrast to the revenue they can help bartenders generate. A reduction in injuries and fatigue, and related callouts, are just some of the benefits. Increased efficiency and speed are two more key advantages over standard stations.
Perlick, the pioneer, is no longer the only company manufacturing ergonomic bar stations. Behind Bars, EuroBar, and Krowne are a few examples of other brands with similar bar stations, so there are other options out there.
Modular Bar Stations
Ergonomics aren’t the only innovation in bar stations. While planning and laying out your bar, you can take advantage of modular offerings.
Different concepts have different needs, it’s that simple. If this were false, bar station manufacturers wouldn’t offer modular options; it wouldn’t make financial sense.
Operators are now able to select the hardware they want. The days of paying for, and putting up with, features that simply take up space and serve no purpose for a particular concept are over.
Bar sinks, speed rails, drain boards, trash stations, drawers and storage, blender stations, coffee benches… There are even manufacturers who make “voids” available. These are dies that hide lines and cords, and cut installation time significantly.
In addition to customizing your layout from the start, modular components mean your concept your grow. Your needs, and those of your bar team, may change over time. Rather than having to rip out bar stations and start over, a modular design allows hardware to be moved or replaced, saving time and money.
While this approach requires more consideration during the planning process, it’s far more efficient and beneficial than settling for pricey equipment that’s not exactly what you and your team want. Further, many items meant for modular bar design are now off the shelf, reducing lead time.
Interactive Bar Tops
The image at the top of this article alludes to this particular innovation. There are bar tops out there that are essentially giant touch screens.
For the most part, these bar tops appear to be focused on wowing guests. They register touch, so they offer an interactive element that some guests will find engaging.
However, I’ve seen more than one demo suggesting that interactive bar tops are also capable of recognizing drinkware. So, a bartender, when serving a drink to a guest, would be able to do so with an accompanying animation. Think of a Dark n Stormy followed by a wave, or a Cosmo with a cosmic, comet trail.
Another feature is the ability to display promotional videos or advertisements. Personally, I’d only want to see the occasional ad for an inhouse promotion, but I can see where the sponsor for a special event would find ads appealing.
However, I expect, some time in the future, for bartenders to have access to more features. POS integration could be powerful, as could the ability to look up a recipe. (Of course, I’d prefer the bar team have signature cocktail recipes memorized, but I see training program potential here.)
Anyone considering an interactive bar top should look for a few features. For one, strength. If glassware can scratch or damage the bar top, it’s not a good idea. Guests don’t always use coasters or bevnaps when they’re provided.
Another consideration is longevity, and therefore terms of any warranty. Finally, operators should take installation into account; if liquid can get underneath the bar top, that’s no good.
Basically, I don’t think these are past the gimmick stage. But I do think operators should keep tabs on interactive bar tops and their eventual improvement.
Self-Service Kiosks
Self-ordering kiosks have, at this point, become ubiquitous. This is particularly true in the QSR space.
Makes sense, right? A guest can stroll through the doors of their favorite fast-food restaurant, head straight to an ordering kiosk, pay, and wait for their order rather than wait in a line if there’s a rush at the counter.
However, I’m talking about a different type of self-service kiosk: the self-pour variety.
Announced earlier this year, as an example, was the iPourIt Kiosk.
You may be familiar with their flagship product, the iPourIt Tap Wall. These impressive, custom installations empower guests to try a range of products on their own schedule. They don’t have to wait for a server to come by every time they want to sample a different beverage. Further, the beverage options aren’t limited to wine or beer; operators can offer cocktails (with or without alcohol), coffee, tea, kombucha, etc.
The custom tap walls also serve as stunning centerpieces, with some venues opting for more than 100 self-serve panels. Of course, that means planning for the construction of the tap wall.
Or, you can opt for a self-pour kiosk.
These operate similarly to tap wall panels, but they’re a self-contained bit of kit that can be rolled and locked into place. I can certainly see the potential for bars or restaurants to leverage such kiosks for brunch service, or to introduce and test new beverages. And there’s definitely potential for hotels to use these kiosks to offer guests convenience and a memorable experience.
Efficient Washers
I’m sure you’re familiar with energy-efficient equipment. In America, it has become common for people seeking equipment in both commercial and residential settings to look for the Energy Star logo.
However, there’s more to consider than just energy costs related to electricity. For example, operators should search for “temperature recovery” or “heat recovery” when choosing glass washers.
These washers make use of internal heat “boosters” to sanitize glassware; they only need a cold water hookup. That’s just one way in which these washers operate in an energy-efficient way, and reduce operational costs.
The heat recovery system also dries and sanitizes glasses more quickly. Further, they’re designed to reduce how much water vapor escapes from the unit, meaning they’re far better for underbar placement.
In addition to washers that are recovery system equipped, operators should look for other energy-efficient features. There are washers that operate at low temperature, and washers that use less water than their standard counterparts.
Other features to consider are soft start (reduces noise, and prevents damage to glassware); reduced time per cycle (two minutes is a good place to start); unit height (ergonomics for the user); individual internal components that are easily accessed, removed, and serviced; and the material used for construction. To explain the latter, a washer built to retain heat and prevent it from escaping too quickly.
When operators plan ahead, including starting with a feasibility and identifying the ideal site, they can maximize their return on investment. Ergonomics and efficiency come at an initial cost, but the ROI has the potential to pay for these benefits and generate profit quickly.
Image: Microsoft Designer

Book Below to Setup a 30-Minute Complimentary Discovery Call and Request for Proposal.