2023: Year of the POS Systems?
by David Klemt

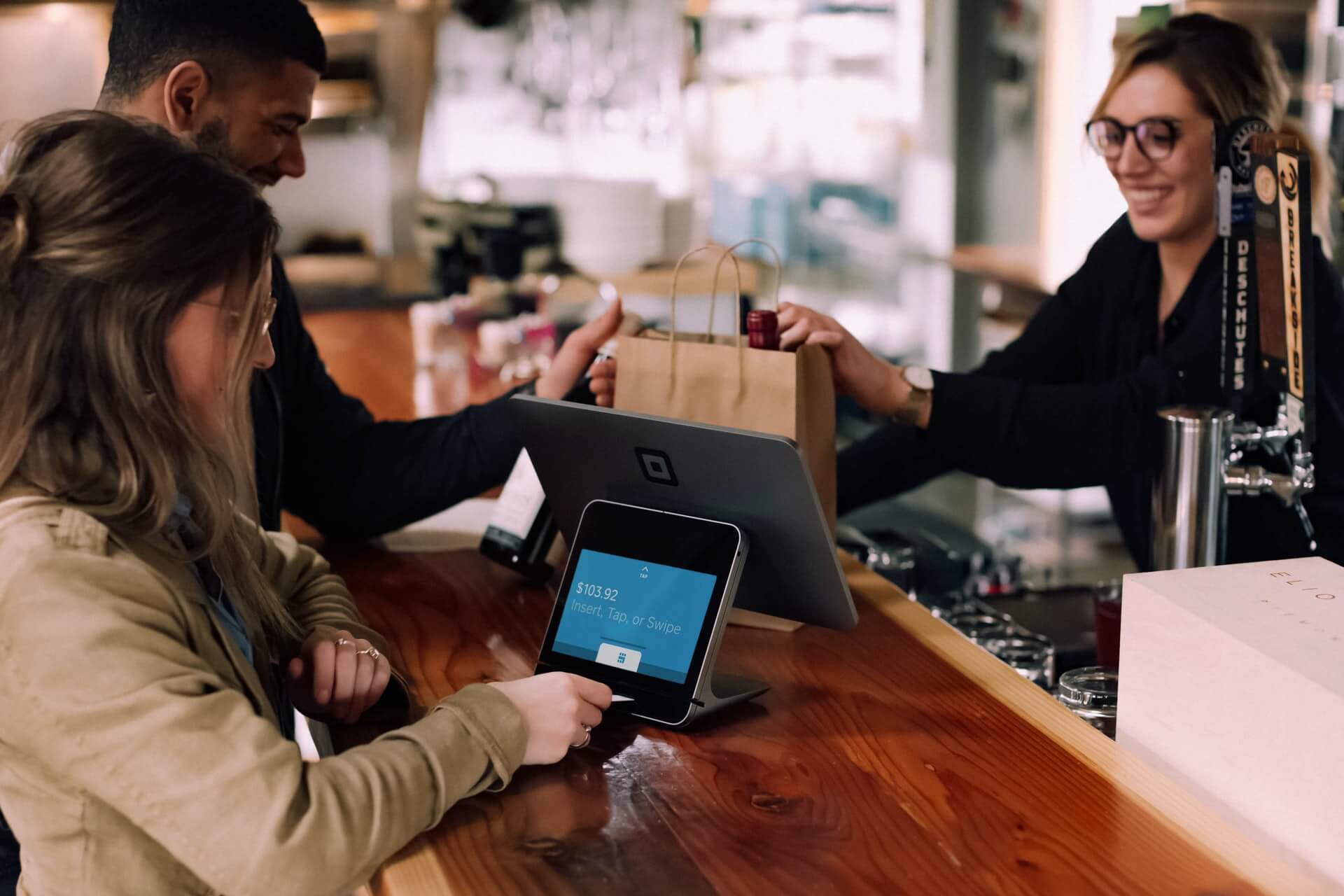
Image from SpotOn press release
According to SpotOn, the industry could be in for a tech revolution next year as independent operators pursue more powerful POS solutions.
The results of a survey conducted by the cloud-based POS platform are rather revealing. In an effort to better understand where the industry is heading, SpotOn surveyed 300 independent and small-chain restaurant operators.
Both full-service and limited-service (LSR) concept operators participated in this SpotOn survey. Intended to identify the challenges operators face currently, the results reveal much more.
Below, the picture these survey results paint for the industry.
Legacy vs. Innovation
This isn’t the first time I’ve stated the following: Our industry hasn’t been the fastest to implement new technology.
However, we did appear to turn that around in 2021. Now, heading into 2023, our industry may be pursuing cutting-edge tech solutions even more fervently. Today’s guest expects more tech, and your team likely wants access to more modern tech that makes their jobs easier.
Per SpotOn’s survey, 81 percent of independent operators still use so-called “legacy” POS systems. These are “traditional” systems from companies that have been around for quite some time.
It’s not difficult to understand why the vast majority of independent operators continue using legacy systems:
- Investing in a new platform requires expenditures of money and time.
- Introducing a new POS platform requires staff training.
- Staff need to grow adept at using the new system.
- It can be daunting to research the available platforms and implementing change.
So, independent and small-chain operators have a choice to make: Stick with the familiar or invest in the future. Change can not only be intimidating, it can be expensive.
However, it seems that most operators are ready to throw comfort to the wayside and embrace innovation.
State-of-the-art Benefits
Should the SpotOn survey prove to be accurate snapshot of the industry, 75 percent of operators will implement new tech next year. According to SpotOn, this is largely in response to growing labor challenges, such as scheduling and retention.
The restaurant, bar, nightclub, and food truck platform found that operators are spending as much as 20 hours per week on administrative tasks. State-of-the-art POS systems can slash those hours by:
- streamlining operations;
- making scheduling simpler;
- calculating tips and payout for payroll; and
- managing overtime, an increasingly common task.
More modern POS platforms can automate labor management tasks, saving operators time, money, and frustration. Automation and streamlining give operators something invaluable: time.
In particular, innovative and helpful tech solutions provide an operator with time to focus on growing their business. When weighing whether to keep a familiar but less feature-rich POS system or invest in a modern platform that seamlessly integrates many solutions, ask yourself a couple important questions:
- What’s my time worth?
- What am I focusing on every day?
- Am I growing my business or stagnating?
- Is my current POS system helping or hindering my team?
- Does my POS system streamline and automate any tasks?
Image: SpotOn